In recent years, the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly waste management solutions has become increasingly crucial. One such solution that has gained attention is the elevated biogas flare.
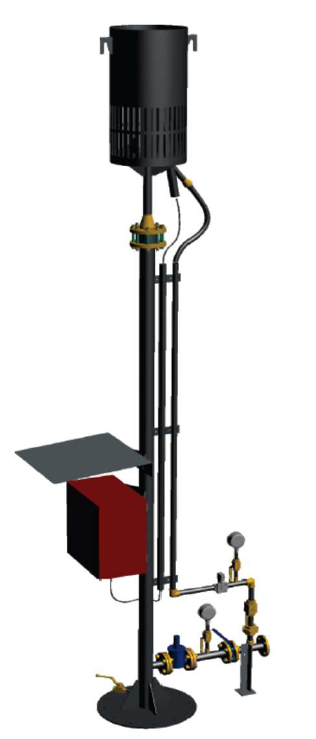
Understanding Elevated Biogas Flares: An elevated biogas flare is a device designed to safely combust and dispose of biogas produced during the anaerobic digestion of organic waste materials. Anaerobic digestion is a natural biological process that breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the generation of biogas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide.
Functioning and Benefits: The flare consist of a burner installed at elevated position, equipped with a high-energy ignition Pilot and a flame detection system via Thermocouple The combustion air is natural conveyed from the bottom part of flame shield and the combustion temperature will be max. 800 °C.
. As biogas is produced in anaerobic digesters, it is directed towards the flare through a network of pipes. Once the biogas reaches the flare, it is ignited, and the combustion process converts the methane into carbon dioxide, water vapor, and heat. This controlled burning prevents the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, thereby mitigating its impact on climate change.
The benefits of elevated biogas flares are manifold. Firstly, they provide an effective means of waste management by safely disposing of biogas generated in anaerobic digestion systems. By converting methane into carbon dioxide, they help to minimize the environmental impact of biogas emissions. Secondly, elevated flares contribute to reducing odors and potential air pollutants associated with biogas, enhancing the overall environmental quality in the vicinity of waste management facilities.
Sustainable Waste Management: Elevated biogas flares play a significant role in sustainable waste management practices. They enable the utilization of organic waste as a renewable energy source, promoting the concept of a circular economy. By extracting energy from biogas, facilities can generate electricity and heat, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to the diversification of the energy mix. This energy can be used on-site or fed into the grid, further supporting local and regional sustainability goals.
Additionally, the integration of elevated biogas flares with anaerobic digestion systems encourages the diversion of organic waste from landfills. Organic waste, when disposed of in landfills, generates methane as it decomposes, which escapes into the atmosphere. By diverting organic waste to anaerobic digestion facilities, not only can valuable energy be extracted, but methane emissions can be significantly reduced, addressing both waste management and climate change concerns simultaneously.
Conclusion: Elevated biogas flares are a sustainable solution for efficient waste management. By safely disposing of biogas through controlled combustion, these flares prevent the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. Moreover, they contribute to sustainable waste management practices by utilizing organic waste as a renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and minimizing landfill emissions. The adoption of elevated biogas flares represents a step towards a greener and more sustainable future, where waste is effectively managed while harnessing its potential for energy generation.

Back to “Biogas Flares” Menu
